The genetic variability of the honeybee population in the Czech Republic had not been thoroughly studied before. This motivated a team of scientists from the Faculty of Agronomy to create a representative sample.
“We divided the entire Czech Republic by regions and districts, collecting an equal number of samples from each geographical area. This resulted in a unique database containing over 5,000 bee samples from across the country,” explained Tomáš Urban from the Institute of Morphology, Physiology, and Animal Genetics at Mendel University in Brno.
With this dataset, scientists were able to systematically analyze the genetic diversity of bees in the Czech Republic. “Historically, the so-called black bee, Apis mellifera mellifera, was traditionally adapted to the area of today’s Czech Republic. Around 200 years ago, a new bee type was gradually imported from the south, from what is now Croatia and Slovenia. This was the Carniolan honeybee, Apis mellifera carnica, which was less aggressive and had higher honey yields. Through mitochondrial DNA analysis, we found that the haplotype of the black bee is no longer present in our samples,” Urban described, suggesting that the native species once typical for the region has likely disappeared.
The historical import of bees from southern Europe had a breeding purpose, but molecular genetics is now expanding its potential. Thanks to the newly developed genetic database, scientists have not only mapped the diversity of honeybee mitochondrial and nuclear DNA in the Czech Republic but also identified genetic differences in individuals that may have higher resistance to diseases. This could be useful in future breeding efforts, particularly against Varroa destructor infestations.
“In Germany, England, and the Nordic countries, there have been efforts to gradually increase the resistance of bee colonies, but practical success has been limited so far. This is due to the complexity of the bee immune response and behavioral traits. That is why it is necessary to systematically search for genes that may be responsible for better resistance to pathogens. This was another key part of our research,” Urban added.
The research team has developed certified methodologies for testing individual bees using microsatellite markers. These markers allow for the identification of bees and the monitoring of their genetic variability in populations. The second methodology can also help identify bees that may have higher resistance to pathogens—an essential step for future breeding programs focused on Varroa resistance.
For more information, contact: Prof. Ing. Tomáš Urban, Ph.D., tomas.urban@mendelu.cz, +420 545 133 182, Institute of Morphology, Physiology, and Animal Genetics, Mendel University in Brno
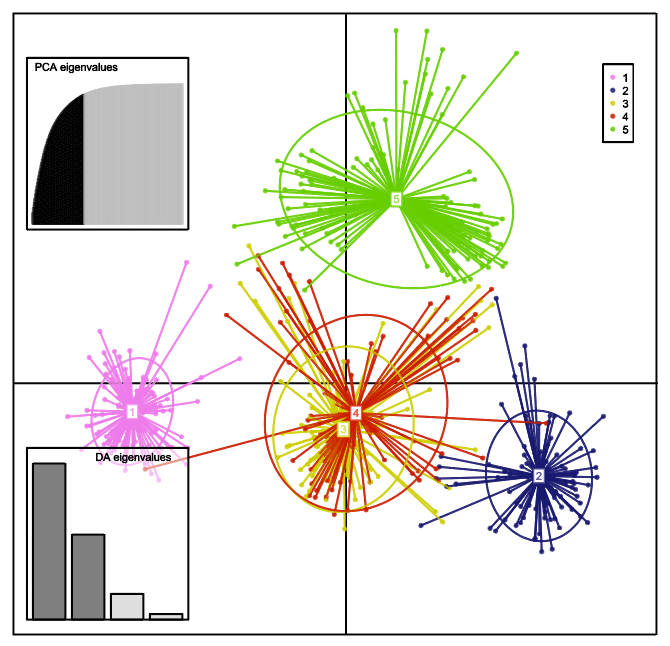
Estimated genetic clusters representing population structure
More news
-
Mendel University has purchased a total of 334 new waste bins for plastic, paper, glass, and mixed waste. The new bins will be available throughout the university campus in Černá Pole, the Botanical Garden and Arboretum, and the Faculty of…12. 3. 2026
-
SPACE DAY and SPACE NET are taking place today at MENDELU, bringing space…
Mendel University in Brno is hosting two events today focused on ongoing space research. SPACE NET MENDELU focuses on how to intelligently integrate current and future applications of space technologies into teaching and research practice. SPACE DAY…4. 3. 2026 -
The university is opening a new MENDELU SHOP in building X
Today, a new MENDELU SHOP is opening on the ground floor of Building X, where you can buy university merchandise such as sweatshirts and T-shirts. A new category of promotional items is the Green Choice collection, where visitors to the shop will…24. 2. 2026 -
Online laboratory tours and virtual autopsy tables. Teaching at MENDELU is…
The teaching of biological and biotechnological subjects at the Faculty of AgriSciences of MENDELU is expanding to include digital innovations. This was prompted by the prolonged distance learning during the pandemic, during which teachers had to…10. 2. 2026 -
Antioxidants in waste materials can be used in the food industry and for plant…
A research team from the Faculty of Horticulture is studying antioxidants in waste materials, especially in woody plants. Plant waste materials often contain higher amounts of certain antioxidants than common foods, and can be used both in the food…5. 2. 2026 -
A scientist from the Faculty of AgriSciences is in Antarctica. She is studying…
Scientist Stanislava Bezdíček Králová is participating in scientific expeditions to Antarctica for the first time under the auspices of the Faculty of AgriSciences at MENDELU. On the icy continent, she is investigating how local microorganisms…27. 1. 2026 -
Cooperation with the Multidisciplinary University of Jerusalem in Israel
The Department of Applied and Landscape Ecology has established an interdisciplinary cooperation with the Multidisciplinary University of Jerusalem in Israel. They designed a joint course was initiated and subsequently piloted during the winter…15. 1. 2026 -
The Faculty of Horticulture supports the production of proteins and anti-cancer…
A scientific team from the Faculty of Horticulture focuses on growing special crops – duckweed and common waterweed – in which they try to stimulate higher production of certain substances, thanks to which the raw material can be used for the…15. 1. 2026 -
MENDELU leads international project focused on the protection and conservation…
Mendel University in Brno is the main coordinator of an international project focused on the protection and conservation of narrow-leaved ash (Fraxinus angustifolia), a key tree species in the floodplain forests of Central and Southern Europe.…18. 12. 2025 -
MENDELU coordinates activities for biodiversity conservation and sustainable…
The Faculty of AgriSciences and the Faculty of Forestry and Wood Technology at MENDELU are coordinating an international project in the Amazon that contributes to biodiversity conservation, sustainable management, and improving quality of life. This…16. 12. 2025