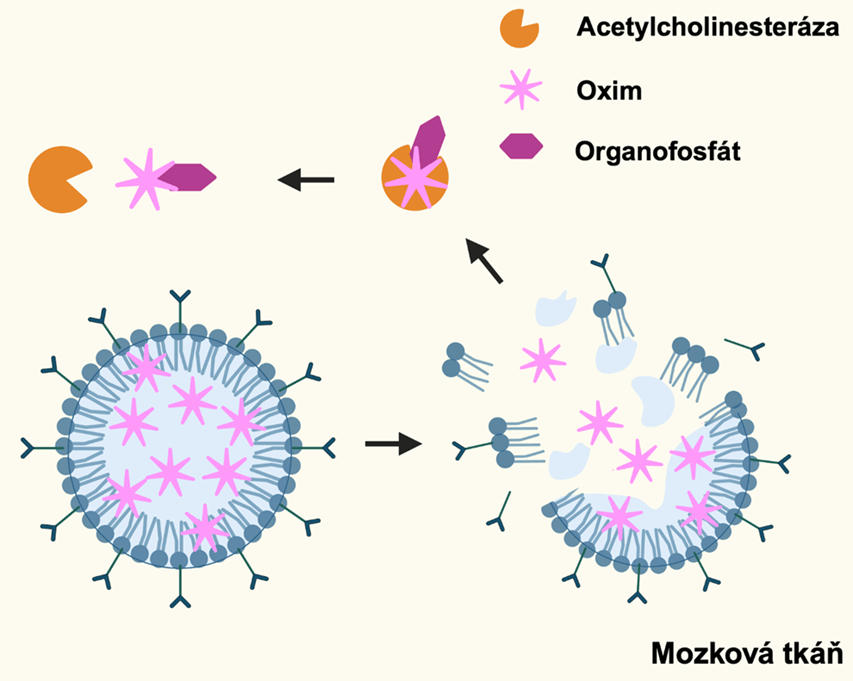
In developing countries they are found as pesticides, in wars they have been misused in the form of chemical weapons such as sarin or the compound VX. We are talking about organic phosphorus compounds, the so-called organophosphates, which cause nerve poisoning. “Organophosphates are able to act as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase, which is an enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and thus terminates nerve transmission. Organophosphates bind to this enzyme and inhibit its activity, resulting in continuous neuromuscular paralysis,” explained Zbyněk Heger, head of the Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry at Mendel University in Brno.
For example, atropine or acetylcholinesterase reactivators (so-called oximes) are currently used to treat organophosphate nerve poisoning. These agents act as antidotes, but their use is still not very effective. “Atropine is a relatively toxic alkaloid. The problem with oximes, on the other hand, is that they do not penetrate the central nervous system very well. The antidote has to pass through the bloodstream, through the filtration system of the liver, kidneys and other organs, and ideally into the brain. The brain is then physiologically protected by several membranes, so the antidotes still have to pass through the blood-brain barrier,” the scientist explained how difficult it is to get the drug to the brain parenchyma. It is there that it can restore the function of enzymes disrupted by organophosphates. At present, however, only a low unit percentage of these antidotes can reach the brain by intravenous injection.
An innovative solution for the transport of oxime in the body may be so-called solid core lipid particles (SLNs). These allow the drug to be encapsulated (‘encapsulated’) and transported to the site of poisoning. “SLNs can be thought of as ~120 nanometer spheres whose surface is composed of phospholipids with a cavity composed of a solid, stabilized lipid core that allows efficient encapsulation of oxime antidotes and other lipophilic agents,” Heger described the technology his team is working on. It is the nano-formulation of SLNs that may hold the key to successfully transporting the drug in the necessary quantities in the human body to the brain.
Zbyněk Heger’s team is also working on the development with other partners, including the Faculty of Science at the University of Hradec Králové and the University of Defence. “We and our partners are particularly interested in antidotes for those who might be exposed to sarin or other nerve agents or pesticides in agriculture. For these purposes, it is necessary to have a stable antidote ready that can be applied ideally immediately after the poisoning, minutes, hours at most, as the antidote is no longer effective after a longer period of time,” Heger added. However, he said the research could have much greater biomedical implications. In the future, for example, for more effective treatment of brain tumours or dementia.
Contact for further information: mgr. Mgr. Zbyněk Heger, PhD., +420 723 429 496, zbynek.heger@mendelu.cz, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, MENDELU University of Applied Sciences
Photo: SLNs with encapsulated oxime (green) in cells.
More news
-
The teaching of biological and biotechnological subjects at the Faculty of AgriSciences of MENDELU is expanding to include digital innovations. This was prompted by the prolonged distance learning during the pandemic, during which teachers had to…10. 2. 2026
-
Antioxidants in waste materials can be used in the food industry and for plant…
A research team from the Faculty of Horticulture is studying antioxidants in waste materials, especially in woody plants. Plant waste materials often contain higher amounts of certain antioxidants than common foods, and can be used both in the food…5. 2. 2026 -
A scientist from the Faculty of AgriSciences is in Antarctica. She is studying…
Scientist Stanislava Bezdíček Králová is participating in scientific expeditions to Antarctica for the first time under the auspices of the Faculty of AgriSciences at MENDELU. On the icy continent, she is investigating how local microorganisms…27. 1. 2026 -
Cooperation with the Multidisciplinary University of Jerusalem in Israel
The Department of Applied and Landscape Ecology has established an interdisciplinary cooperation with the Multidisciplinary University of Jerusalem in Israel. They designed a joint course was initiated and subsequently piloted during the winter…15. 1. 2026 -
The Faculty of Horticulture supports the production of proteins and anti-cancer…
A scientific team from the Faculty of Horticulture focuses on growing special crops – duckweed and common waterweed – in which they try to stimulate higher production of certain substances, thanks to which the raw material can be used for the…15. 1. 2026 -
MENDELU leads international project focused on the protection and conservation…
Mendel University in Brno is the main coordinator of an international project focused on the protection and conservation of narrow-leaved ash (Fraxinus angustifolia), a key tree species in the floodplain forests of Central and Southern Europe.…18. 12. 2025 -
MENDELU coordinates activities for biodiversity conservation and sustainable…
The Faculty of AgriSciences and the Faculty of Forestry and Wood Technology at MENDELU are coordinating an international project in the Amazon that contributes to biodiversity conservation, sustainable management, and improving quality of life. This…16. 12. 2025 -
MENDELU launches High School University, applications open today
At the beginning of 2026, Mendel University in Brno will launch the first year of its High School University for second- and third-year high school students. The aim is to give twenty-five high school students a glimpse into the university…8. 12. 2025 -
The popularity of intergenerational learning is growing in Czechia and Slovakia
In December, Mendel University in Brno and the University of Žilina in Žilina are continuing their intensive cooperation on the development of intergenerational programs, which have been growing in popularity in both countries in recent years. The…4. 12. 2025 -
Testing VR Application at Mendel University: Innovation in Water Education
During the international Thematic Lecture „DIGITALISATION AND NATURE-BASED-SOLUTIONS FOR WASTEWATER TREATMENT“ event for water management experts, organized by the CREA Hydro&Energy cluster, experts tested a new VR application focused on teaching…3. 12. 2025